Posner and Easterbrook suggest that these industry behaviours together are suspicious.
- Fixed relative market shares among top firms over time.
- Declining absolute market shares of the industry leaders.
- Persistent price discrimination.
- Certain types of exchanges of price information.
- Regional price variations.
- Identical sealed bids for tenders.
- Price, output, and capacity changes at the time of the suspected initiation of collusion.
- Industry-wide resale price maintenance or non-price vertical restraints.
- Relatively infrequent price changes; smaller price reactions as a result of known cost changes.
- Demand is highly responsive to price changes at market price.
- Level and pattern of profits relatively favourable to smaller firms.
- Particular pricing and marketing strategies.
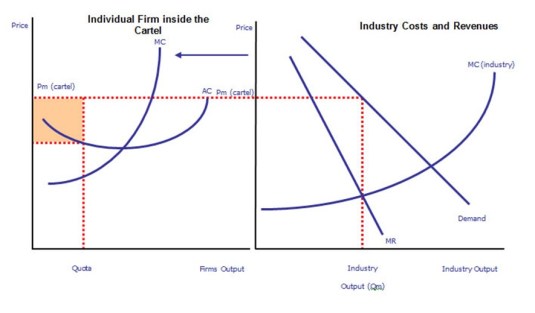
Aaron Director’s most creative suggestion of evidence of price collusion is disputes between the marketing and finance departments of a large company. The market department wants to cut prices because there would be a large increase in sales. The finance department says no because this would take the price below the monopoly or agreed cartel price.
Recent Comments