An anti-competitive merger should boost the share prices of the remaining rivals. If there is less competition and higher prices after the merger, the remaining rival firms in the market can follow those price rises up without fear of being undercut.
The Sky TV merger with Vodafone announced today is an example of that. Its competition in broadband, which is Spark, experienced a small fall in its share price. Investors in that company do not anticipate higher prices in the future as a result of the merger announced today.
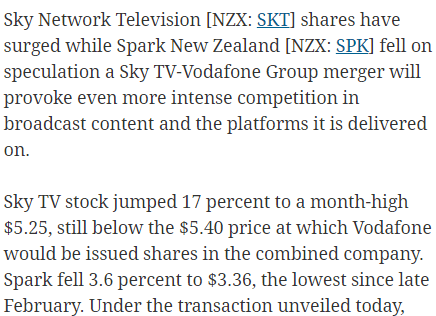
Source: Sky TV shares surge, Spark falls on Vodafone merger | The National Business Review.
There is a long history of studying share market reactions to mergers first by Eckbo (1983) and Stillman (1983). The change in the value of competitors’ equity can measure the (discounted) additional profits that is expected to accrue to them as a consequence of the merger.
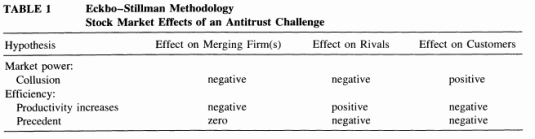
Source: The Competitive Effects of Mergers: Stock Market Evidence from the U.S. Steel Dissolution Suit George L. Mullin, Joseph C. Mullin and Wallace P. Mullin, The RAND Journal of Economics Vol. 26, No. 2 (Summer, 1995), pp. 314-330.
A positive reaction of remaining rivals to a merger indicates that the merger enhances competitors’ profits. This effect has been called the collusion hypothesis. Collusion is easier after the merger so share prices go up. If share prices fall, more effective collusion is not on the horizon. The adjacent snapshot of a table shows what happens to share prices when a competition agency opposes a merger.
Another way to study the competitive effects of mergers is the share market reaction in downstream markets. Do buyers anticipate lower prices from the merged supplier and its rivals?
Another test of the anti-competitive effects of the merger is whether the remaining rival firms oppose it. Was it Frank Easterbrook in the 1980s or Aaron Director in the 1950s who said that the clearest evidence of a pro-competitive merger was if rival firms ask the competition law enforcement agency to take action against it? Do the competitors oppose the merger? If they do, the merger must lower prices and put their profits under more pressure.
Recent Comments