From https://www.bradford-delong.com/2011/10/hoisted-from-the-archives-evaluating-fiscal-stimulus.html and see too https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB123423402552366409
At https://www.chicagobooth.edu/research/igm/events-forums/myron-scholes-forum/speaker-series/2009-01-16 Murphy says
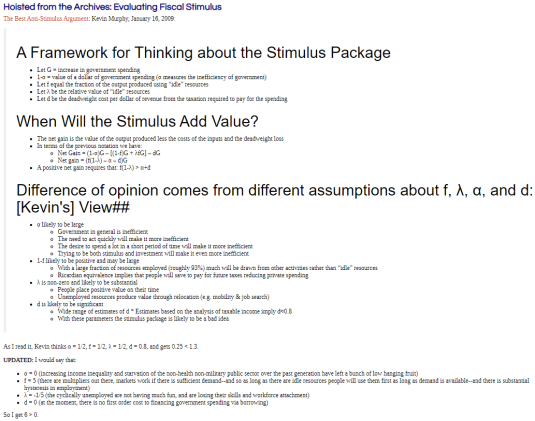
Kevin Murphy sketched out a simple equation—into which anyone could easily plug their own assumptions—to compare the benefits and costs of stimulus spending. The advantage, he argued, is the equation helps everyone to be clear about exactly what they are assuming and why it supports their approach to the stimulus. According to Murphy, the main items everyone should be clear about are: the fraction of the economy’s resources that are idle; the value of keeping those resources idle (e.g., most people value their time, and will not work without compensation); the deadweight loss from raising taxes in the future to pay for the spending; and the cost of allocating spending through government, if it is allocated less efficiently as a result (this can be negative —i.e., a benefit—if government is better than the private sector at allocating resources).
Murphy did not consider the stimulus a good proposal, but he explained how his assumptions about each element of his framework differed from those of president-elect Obama’s team. “It’s easy to see what you have to assume in order to make the stimulus make sense,” Murphy said. Regarding the tax cut measures in the stimulus plan, Murphy thought they were designed in an especially inefficient way. Since marginal tax rates are what matter for incentives, he argued, it was not helpful that the Obama plan would give tax cuts in the form of direct credits to certain taxpayers without lowering rates. That the president would likely address the resulting deficit by raising rates in the future would exacerbate the problem.
And Robert Lucas adds
Robert Lucas pointed out that the US economy was already 4 percent below its long-term trend level in January 2008. In addition, consensus forecasts—which “mean a lot” over short horizons such as a year—suggested the economy would be 8 percent below after another year. This would be larger than any other postwar recession, though nowhere near as bad as the 30 percent gap in the 1930s. “It’s not the worst in my lifetime, but it’s the worst in Obama’s,” Lucas said, “and it would be foolish not to take some actions to deal with it.”
Monetary measures to deal with the recession make a lot of sense, said Lucas, who added that many of the Fed’s actions were beneficial. The trouble was the fiscal stimulus did not seem designed to deal with the real problem. A good approach, Lucas said, would be to use the fiscal stimulus “as another way of getting cash into circulation in the private sector.” He mentioned hypothetical examples that Milton Friedman—dropping money from helicopters—and John Maynard Keynes—paying people to dig and refill ditches—had posed as ways of achieving this. “If fiscal stimuli are designed to be effective, they’re going to be effective because they carry along a monetary policy of the sort that raises the dollar spending level,” Lucas said. Based on the plans and information he had seen from president-elect Obama’s advisors, however, Lucas said that this did not seem to be what the new administration was planning. Instead, he said, “all they’re talking about is transferring resources, additional levels of spending, from one use to another,” which, he argued, would have no substantial effect on the average level of spending and thus would not help fight the recession.
Recent Comments