
Doug Allen has an amusing summary of the history of thought on his website. https://t.co/nyXseQH37j pic.twitter.com/c08rYCeJ5i
— Josh Hendrickson (@RebelEconProf) June 24, 2020
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
25 Jun 2020 Leave a comment
in Adam Smith, Alfred Marshall, applied price theory, applied welfare economics, Armen Alchian, Austrian economics, comparative institutional analysis, constitutional political economy, economic history, economics of crime, economics of regulation, history of economic thought, industrial organisation, James Buchanan, James Buchanan, labour economics, law and economics, Marxist economics, Milton Friedman, property rights, Public Choice, Rawls and Nozick, Robert E. Lucas, Ronald Coase, Ronald Coase, theory of the firm

22 Apr 2020 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, Armen Alchian, comparative institutional analysis, economic history, economics of bureaucracy, economics of information, economics of regulation, entrepreneurship, environmental economics, financial economics, George Stigler, health economics, history of economic thought, industrial organisation, law and economics, property rights, Public Choice, resource economics, Richard Posner, Ronald Coase, Ronald Coase, Ronald Coase, survivor principle, theory of the firm, transport economics, urban economics
05 Mar 2019 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, comparative institutional analysis, economics of information, economics of love and marriage, law and economics, property rights, Ronald Coase, theory of the firm Tags: marriage and divorce
03 Mar 2019 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, comparative institutional analysis, economics of regulation, environmental economics, history of economic thought, law and economics, public economics, Ronald Coase, Ronald Coase Tags: Coase theorem
11 Apr 2016 Leave a comment
in history of economic thought, industrial organisation, law and economics, property rights, Ronald Coase, theory of the firm
Summary:
Source: Forever Contemporary – The Economics of Ronald Coase | Institute of Economic Affairs
17 Aug 2014 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, Armen Alchian, comparative institutional analysis, entrepreneurship, industrial organisation, Ronald Coase, survivor principle, theory of the firm Tags: long-term contracts, mutual dependency, relationship dependent assets, transaction costs, vertical integration
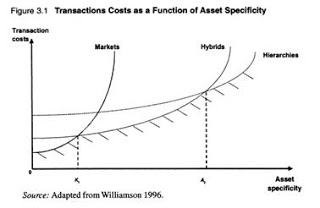
via “Trapped” in Rental Contracts | Organizations and Markets.
24 Jul 2014 3 Comments
in Armen Alchian, industrial organisation, Ronald Coase, survivor principle, theory of the firm Tags: Armlen Alchian, Eugene Fara, Harold Demsetz, Ronald Coase, separation of ownership and control, theory of the firm

Eugene Fama divides firms into two types: the managerial firm, and the entrepreneurial firm.
The owners of a managerial firm advance, withdraw, and redeploy capital, carry the residual investment risks of ownership and have the ultimate decision making rights over the fate of the firm (Klein 1999; Foss and Lien 2010; Fama 1980; Fama and Jensen 1983a, 1983b; Jensen and Meckling 1976).
Owners of a managerial firm, by definition, will delegate control to expert managerial employees appointed by boards of directors elected by the shareholders (Fama and Jensen 1983a, 1983b). The owners of a managerial firm will incur costs in observing with considerable imprecision the actual efforts, due diligence, true motives and entrepreneurial shrewdness of the managers and directors they hired (Jensen and Meckling 1976; Fama and Jensen 1983b).
Owners need to uncover whether a substandard performance is due to mismanagement, high costs, paying the employees too much or paying too little, excessive staff turnover, inferior products, or random factors beyond the control of their managers (Jensen and Meckling 1976; Fama and Jensen 1983b, 1985). Any paucity in knowledge slows the reactions of owners in correcting managerial errors including slip-ups in the recruitment and the retention of experienced older employees.
The entrepreneurial firms are owned and managed by the same people (Fama and Jensen 1983b). Mediocre personnel policies and sub-standard staff retention practices within entrepreneurial firms are disciplined by these errors in judgement by owner-managers feeding straight back into the returns on the capital that these owner-managers themselves invested. Owner-managers can learn quickly and can act faster in response the discovery of errors in judgement. The drawback of entrepreneurial firms is not every investor wants to be hands-on even if they had the skills and nor do they want to risk being undiversified.
Many of the shareholders in managerial firms have too small a stake to gain from monitoring managerial effort, employee performance, capital budgets, the control of costs and the stinginess or generosity of wage and employment policies (Manne 1965; Fama 1980; Fama and Jensen 1983a, 1983b; Williamson 1985; Jensen and Meckling 1976). This lack of interest by small and diversified investors does not undo the status of the firm as a competitive investment.

Large firms are run by managers hired by diversified owners because this outcome is the most profitable form of organisation to raise capital and then find the managerial talent to put this pool of capital to its most profitable uses (Fama and Jensen 1983a, 1983b, 1985; Demsetz and Lehn 1985; Alchian and Woodward 1987, 1988).
More active investors will hesitate to invest in large managerial firms whose governance structures tolerate excessive corporate waste and do not address managerial slack and error. Financial entrepreneurs will win risk-free profits from being alert and being first to buy or sell shares in the better or worse governed firms that come to their notice.
The risks to dividends and capital because of manifestations of corporate waste, reduced employee effort, and managerial slack and aggrandisement in large managerial firms are risks that are well known to investors (Jensen and Meckling 1976; Fama and Jenson 1983b). Corporate waste and managerial slack also increase the chances of a decline in sales and even business failure because of product market competition (Fama 1980; Fama and Jensen 1983b). Investors will expect an offsetting risk premium before they buy shares in more ill-governed managerial firms. This is because without this top-up on dividends, they can invest in plenty of other options that foretell a higher risk-adjusted rate of return.
The discovery of monitoring or incentive systems that induce managers to act in the best interest of shareholders are entrepreneurial opportunities for pure profit (Fama and Jensen 1983b, 1985; Alchian and Woodward 1987, 1988; Demsetz 1983, 1986; Demsetz and Lehn 1985; Demsetz and Villalonga 2001). Investors will not entrust their funds to who are virtual strangers unless they expect to profit from a specialisation and a division of labour between asset management and managerial talent and in capital supply and residual risk bearing (Fama 1980; Fama and Jensen 1983a, 1983b; Demsetz and Lehn 1985). There are other investment formats that offer more predictable, more certain rate of returns.

Competition from other firms will force the evolution of devices within the firms that survive for the efficient monitoring the performance of the entire team of employees and of individual members of those teams as well as managers (Fama 1980, Fama and Jensen 1983a, 1983b; Demsetz and Lehn 1985). These management controls must proxy as cost-effectively as they can having an owner-manager on the spot to balance the risks and rewards of innovating.
The reward for forming a well-disciplined managerial firm despite the drawbacks of diffuse ownership is the ability to raise large amounts in equity capital from investors seeking diversification and limited liability (Demsetz 1967; Jensen and Meckling 1976; Fama 1980; Fama and Jensen 1983b; Demsetz and Lehn 1985).Portfolio investors may know little about each other and only so much about the firm because diversification and limited liability makes this knowledge less important (Demsetz 1967; Jensen and Meckling 1976; Alchian and Woodward 1987, 1988).
It is still unwise to still suppose that portfolio investors will keep relinquishing control over part of their capital to virtual strangers who do not manage the resources entrusted to them in the best interests of the shareholders (Demsetz 1967; Williamson 1985; Fama 1980, 1983b; Alchian and Woodward 1987, 1988).
Managerial firms who are not alert enough to develop cost effective solutions to incentive conflicts and misalignments will not grow to displace rival forms of corporate organisation and methods of raising equity capital and loans, allocating legal liability, diversifying risk, organising production, replacing less able management teams, and monitoring and rewarding employees (Fama and Jensen 1983a, 1983b; Fama 1980; Alchian 1950).
Entrepreneurs win profits from creating corporate governance structures that can credibly assure current and future investors that their interests are protected and their shares are likely to prosper (Fama 1980; Fama and Jensen 1983a, 1983b, 1985; Demsetz 1986; Demsetz and Lehn 1985). Corporate governance is the set of control devices that are developed in response to conflicts of interest in a firm (Fama and Jensen 1983b).
20 Jul 2014 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, Armen Alchian, industrial organisation, Ronald Coase, theory of the firm Tags: markets and hierarchies, Oliver Williamson, Robert Lucas, Ronald Coase, span of control, theory of the firm, Walter Oi

One constraint on the growth of any firm is entrepreneurs have a limited span of control (Coase 1937; Williamson 1967, Lucas 1978; Oi 1983a, 1983b). A span of control is the number of subordinates that an individual supervisor has to control and lead either directly or through a hierarchical managerial chain (Fox 2009).
There are only so many tasks that even the most able entrepreneurs can carry out in one day. Over-stretched spans of control motivate entrepreneurs to hire professional managers and delegate to them a wide range of decision-making rights over the firms they own (Williamson 1975; Foss, Foss and Klein 2008).
Entrepreneurs and the professional managers they hired to assist them must divide their respective time between monitoring employees, identifying new business opportunities, forecasting buyer demand and running the other aspects of their business (Lucas, 1978; Oi 1983, 1983b, 1988; Foss, Foss, and Klein 2008). The larger is the firm, the more employees there are for the entrepreneur to direct, monitor and reward. These costs of directing and monitoring employees will increase with the size of the firm and larger firms will encounter information problems not present in smaller firms (Alchian and Demsetz 1972; Stigler 1962).

The cost of entrepreneurial time spent monitoring employees will increase with the size of the firm (Lucas 1978; Oi 1983b). The time of the more talented entrepreneurs is more valuable because they had the superior managerial skills and entrepreneurial alertness to make their firms large in the first place and remain deft enough to survive in competition. Time spent on the supervision of employees is time that is spent away from other uses of the talents that got these more able entrepreneurs to the top and keeps them there (Williamson 1967; Lucas 1978; Oi 1983b, 1988, 1990; Idson and Oi 1999; Black et al 1999).
Firms in the same industry tend to exhibit systematic differences in their organization of production and the structure of their workforces because entrepreneurial ability is the specific and scarce production input that limits the size of a firm (Lucas, 1978; Oi 1983b). The less able entrepreneurs tend to run the smaller firms while the more able entrepreneurs tend to lead both the currently large firms and the smaller firms that are growing at the expense of market rivals (Lucas 1978, Oi 1983b; Stigler 1958; Alchian 1950).
23 Jun 2014 Leave a comment
in comparative institutional analysis, constitutional political economy, Ronald Coase, Ronald Coase Tags: Harold Demsetz, Roanald Coase
 |
 |
It is my belief that the failure of economists to reach correct conclusions about the treatment of harmful effects cannot be ascribed simply to a few slips in analysis. It stems from basic defects in the current approach to problems of welfare economics
Ronal Coase (1960)
The view that now pervades much public policy economics implicitly presents the relevant choice as between an ideal norm and an existing ‘imperfect’ institutional arrangement.
This nirvana approach differs considerably from a comparative institution approach in which the relevant choice is between alternative real institutional arrangements…
the design of institutional arrangements that provide incentives to encourage experimentation (including the development of new products, new knowledge, new reputations, and new ways of organizing activities) without overly insulating these experiments from the ultimate test
of survivalHarold Demsetz (1969)
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
Scholarly commentary on law, economics, and more
Beatrice Cherrier's blog
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
Why Evolution is True is a blog written by Jerry Coyne, centered on evolution and biology but also dealing with diverse topics like politics, culture, and cats.
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
A rural perspective with a blue tint by Ele Ludemann
DPF's Kiwiblog - Fomenting Happy Mischief since 2003
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
The world's most viewed site on global warming and climate change
Tim Harding's writings on rationality, informal logic and skepticism
A window into Doc Freiberger's library
Let's examine hard decisions!
Commentary on monetary policy in the spirit of R. G. Hawtrey
Thoughts on public policy and the media
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
Politics and the economy
A blog (primarily) on Canadian and Commonwealth political history and institutions
Reading between the lines, and underneath the hype.
Economics, and such stuff as dreams are made on
"The British constitution has always been puzzling, and always will be." --Queen Elizabeth II
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
WORLD WAR II, MUSIC, HISTORY, HOLOCAUST
Undisciplined scholar, recovering academic
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
Res ipsa loquitur - The thing itself speaks
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
Researching the House of Commons, 1832-1868
Articles and research from the History of Parliament Trust
Reflections on books and art
Posts on the History of Law, Crime, and Justice
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
Exploring the Monarchs of Europe
Cutting edge science you can dice with
Small Steps Toward A Much Better World
“We do not believe any group of men adequate enough or wise enough to operate without scrutiny or without criticism. We know that the only way to avoid error is to detect it, that the only way to detect it is to be free to inquire. We know that in secrecy error undetected will flourish and subvert”. - J Robert Oppenheimer.
The truth about the great wind power fraud - we're not here to debate the wind industry, we're here to destroy it.
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
Economics, public policy, monetary policy, financial regulation, with a New Zealand perspective
Celebrating humanity's flourishing through the spread of capitalism and the rule of law
Restraining Government in America and Around the World
Recent Comments