
Russian offsetting behaviour
16 Oct 2017 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, sports economics Tags: offsetting behaviour, unintended consequences

Financial regulation and financial crisis | Sam Peltzman
11 Oct 2017 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, economics of regulation, financial economics, global financial crisis (GFC), macroeconomics, monetary economics, Sam Peltzman Tags: offsetting behaviour, unintended consequences
Danish minimum wage goes up by 40% at age 18
30 Sep 2017 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, labour economics, minimum wage Tags: expressive voting, offsetting behaviour
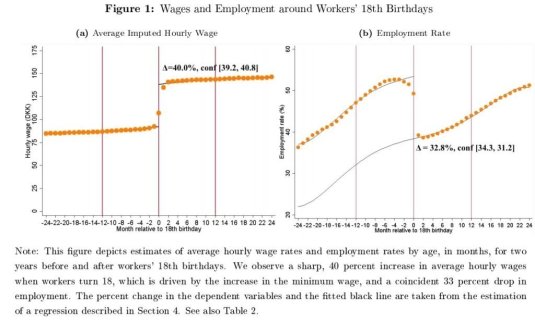
Source: http://www.nationalreview.com/corner/449066/minimum-wage-study-denmark-finds-big-hit-employment
Why boxing headguards may be making the sport more dangerous
14 Sep 2017 Leave a comment
in health and safety, health economics, labour economics, occupational choice, sports economics Tags: offsetting behaviour
Monty Python on the economics of begging and do-gooders
24 Jun 2017 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, labour economics, movies, occupational choice, poverty and inequality Tags: begging, do gooders, Monty Python, offsetting behaviour, unintended consequences
Faces of $15: Seattle Subway Slashes Staff
22 Jun 2017 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, applied welfare economics, economics of regulation, labour economics, minimum wage Tags: offsetting behaviour
Early temperance movements were a public health setback
10 Jun 2017 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, economic history, economics of regulation, health economics Tags: economics of prohibition, offsetting behaviour, The fatal conceit, unintended consequences
Watching a history of prohibition. Started in 1850s, at least half a century before safe drinking water was freely available such as through tap water.
Beer was much safer than drinking water until a good way into the 20th century. Initial temperance movement was against hard liquor but quickly was about abstinence.
Humanitarians redeemed Sudanese slaves by buying them out of slavery. Did it work out?
02 Jun 2017 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, development economics, economics of crime, growth disasters, law and economics Tags: economics of slavery, offsetting behaviour, unintended consequences
Offsetting behaviour alert: boxing headguards @EricCrampton
04 May 2017 Leave a comment
in health and safety, labour economics, occupational choice, sports economics Tags: health and safety, offsetting behaviour, unintended consequences
When people complain about the black market or organised crime
02 May 2017 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, economic history, economics of crime, economics of regulation, health economics, law and economics Tags: black markets, offsetting behaviour, organised crime, unintended consequences
#GarethMorgan wants sitting tenant laws
28 Apr 2017 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, applied welfare economics, economics of regulation, income redistribution, politics - New Zealand, Public Choice, rentseeking Tags: 2017 New Zealand election, offsetting behaviour, rent control, unintended consequences
Morgan wants to restrict the ability to evict tenants for reasons other than damage to the property and non-payment of rent. This includes not been able to evict a tenant on sale of the property.
We intend to change the regulations around residential tenancy law so leases make it far easier for a tenant to remain in the premises long term…
This will be achieved by restricting the conditions under which a landlord can evict a tenant to those of non-payment of rent or property damage. Sale of a property is not necessarily a legitimate reason for eviction. Tenants will be able to give 90 days notice.
That policy will make winding up of estates difficult. Houses will be have to be left vacant rather than rented while affairs are put in order. That is to name one of many flaws in a policy announced by a party that prioritises being different over been useful and right.
Source: RENTING Werner Z. Hirsch at encyclopedia of law and economics.




Recent Comments