Colonialism, Slavery, and Foreign Aid (with William Easterly) 12/8/25
01 Feb 2026 1 Comment
in applied price theory, comparative institutional analysis, constitutional political economy, development economics, economic history, growth disasters, growth miracles, history of economic thought, labour economics, labour supply, law and economics, property rights Tags: age of empires, economics of colonialism, economics of slavery
Are the French lazy?
30 Jan 2026 Leave a comment
in labour economics, macroeconomics, economics of regulation, economic growth, applied price theory, labour supply, fiscal policy Tags: France, taxation and labour supply
Olivier Blanchard writes: The French are not lazy. They just enjoy leisure more than most (no irony here) And this is perfectly fine: As productivity increases, it is perfectly reasonable to take it partly as more leisure (fewer hours per week, earlier retirement age), and only partly in income. He has follow-up points and clarifications…
Are the French lazy?
Exciting New Research on the Laffer Curve
30 Jan 2026 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, econometerics, economic growth, economic history, fiscal policy, history of economic thought, labour economics, labour supply, macroeconomics Tags: taxation and investment, taxation and labour supply

Unless you’re a policy wonk, I realize “exciting” may not be the right word to describe new developments in public-finance economics. For nerds, however, three economists at the Joint Committee on Taxation have some important new research on the Laffer Curve. The study, authored by Rachel Moore, Brandon Pecoraro, and David Splinter, concludes that the […]
Exciting New Research on the Laffer Curve
AI and Jobs: Interview with David Autor
25 Jan 2026 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, industrial organisation, labour economics, labour supply Tags: creative destruction
Sara Frueh interviews David Autor on the subject: “How Is AI Shaping the Future of Work?” (Issues in Science and Technology, January 6, 2026). Here are some snippets that caught my eye, but it’s worth reading the essay and even clicking on some of the suggested additional readings: How broadly are AI tools already being…
AI and Jobs: Interview with David Autor
AI, labor markets, and wages
18 Jan 2026 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, econometerics, economic growth, industrial organisation, labour economics, labour supply, macroeconomics, poverty and inequality Tags: creative destruction, pessimist bias
There is a new and optimistic paper by Lukas Althoff and Hugo Reichardt: Artificial intelligence is changing which tasks workers do and how they do them. Predicting its labor market consequences requires understanding how technical change affects workers’ productivity across tasks, how workers adapt by changing occupations and acquiring new skills, and how wages adjust…
AI, labor markets, and wages
Some Snapshots of the US Demographic Future
13 Jan 2026 Leave a comment
in labour economics, labour supply, politics - USA, population economics Tags: ageing society, population bust

Demography is the study of the structure of human populations, including factors like births, deaths, aging, as well as health and economic factors. Some demographic changes happen slowly, over decades, but in a predicable way. For example, if you want to look at projections for the year 2050 of the ratio of the US working-age…
Some Snapshots of the US Demographic Future
Profile of George Borjas and his influence
12 Jan 2026 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, income redistribution, labour economics, labour supply, politics - USA, Public Choice Tags: economics of immigration
More recently, his research has found new attention and urgency in President Donald Trump’s second term: Borjas, 75, worked as a top economist on the Council of Economic Advisers, a post he stepped down from last week. Borjas is an immigrant and refugee who escaped Cuba for the United States in 1962 and later obtained…
Profile of George Borjas and his influence
Reflections on the Caplan-Bruenig Poverty Debate
09 Jan 2026 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, history of economic thought, labour economics, labour supply, liberalism, libertarianism, Marxist economics, politics - USA, poverty and inequality, welfare reform Tags: child poverty, family poverty

Last month, Econoboi hosted a debate on poverty between myself and Matt Bruenig. Here are my reflections on that debate.I was pleasantly surprised by Bruenig’s openness to most of my proposed supply-side reforms. He wasn’t just pro-immigration, but also pro-deregulation of housing and pro-nuclear. He was happy to admit that these policies aren’t just good…
Reflections on the Caplan-Bruenig Poverty Debate
Building more will boost labor’s share
06 Jan 2026 1 Comment
in applied price theory, labour economics, labour supply
This paper argues that the decline in the labor share is not driven by the overall quantity of capital, but by its changing composition. Constructing annual macro data for 16 advanced countries over two centuries, we show that, since 1980, the relative decline in buildings capital and the associated increase in real prices of buildings…
Building more will boost labor’s share
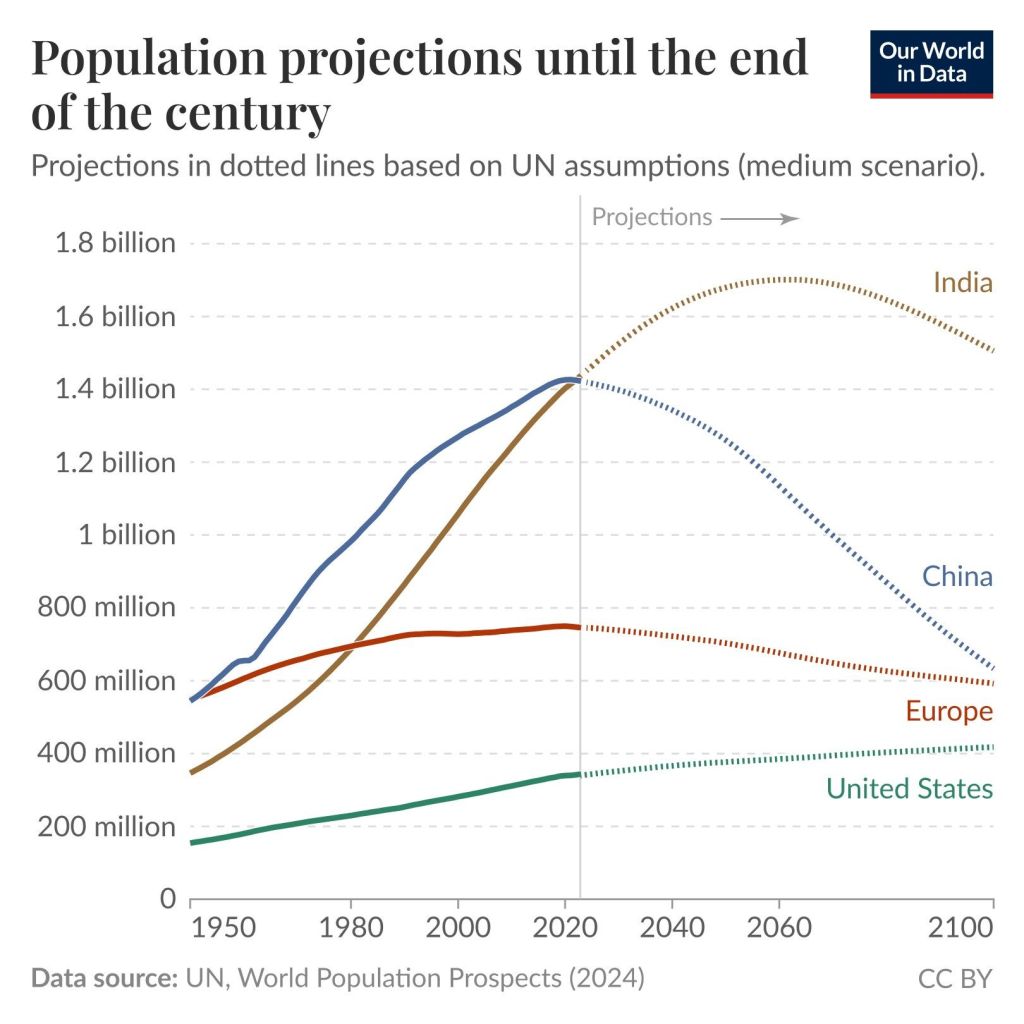
So much for overpopulation
02 Jan 2026 Leave a comment
in development economics, economic history, labour economics, labour supply, population economics Tags: ageing society, population bust
What Star Wars AND Star Trek can teach us about economics
01 Jan 2026 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, comparative institutional analysis, defence economics, economics of regulation, international economics, labour economics, labour supply, movies, television, TV shows, unions
This is not a “Star Wars vs Star Trek” post. I’m non-partisan. I enjoy both Star Wars and Star Trek about equally. And it turns out that I am not alone. Last December, John Hawkins (University of Canberra) wrote in The Conversation about what Star Wars can teach us about economics. This year, Hawkins (with Tesfaye…
What Star Wars AND Star Trek can teach us about economics
US Growth: From Hours Worked or Productivity Gains?
30 Dec 2025 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, econometerics, economic growth, economic history, labour economics, labour supply, macroeconomics

US economic growth can be divided into two parts: more hours worked, or more productivity per hour worked. In the past, the US labor force has been rising over time: the US labor force totaled 107 million people in 1980, 142 million in 2000, and was up to 171 million this year. However, after several…
US Growth: From Hours Worked or Productivity Gains?
Canada fact of the day
29 Dec 2025 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, development economics, labour economics, labour supply, poverty and inequality, welfare reform Tags: Canada
Since 2015, Canada has tripled its Indigenous spending – paying more than on national defense. Over those same years, Indigenous people have suffered a catastrophic collapse in health and well-being: on average almost a full decade of lost life expectancy. That is from David Frum. The post Canada fact of the day appeared first on…
Canada fact of the day
AI summary of my living wage paper
24 Dec 2025 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, history of economic thought, income redistribution, job search and matching, labour economics, labour supply, macroeconomics, minimum wage, politics - New Zealand, poverty and inequality, Public Choice, rentseeking Tags: living wage




Recent Comments