Nicola Willis writes: Having the C-word directed at me by a journalist in a mainstream publication wasn’t on my bingo-list for Mother’s Day 2025. Nor was being accused of “girl-math”. But there you have it, that’s what was thrown at me and my female colleagues in a recent newspaper column as hopelessly devoid of facts as it […]
Willis responds to Vance celling her a c**t
Willis responds to Vance celling her a c**t
12 May 2025 Leave a comment
in discrimination, gender, health and safety, human capital, labour economics, labour supply, occupational choice, politics - New Zealand, poverty and inequality Tags: gender wage gap, sex discrimination
Does he know what a woman is now?
07 May 2025 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, discrimination, economics of education, gender, health and safety, human capital, labour economics, labour supply, occupational choice, politics - New Zealand, poverty and inequality, Public Choice, rentseeking Tags: gender wage gap, sex discrimination
Labour leader Chris Hipkins has joined the chorus of those opposing changes to pay equity legislation. Does this mean he knows what a woman is now? It is easy for opposition parties and their allies to criticise proposed changes but Heather du Plessis-Allan points out the problem with existing legislation: . . . Those pay […]
Does he know what a woman is now?
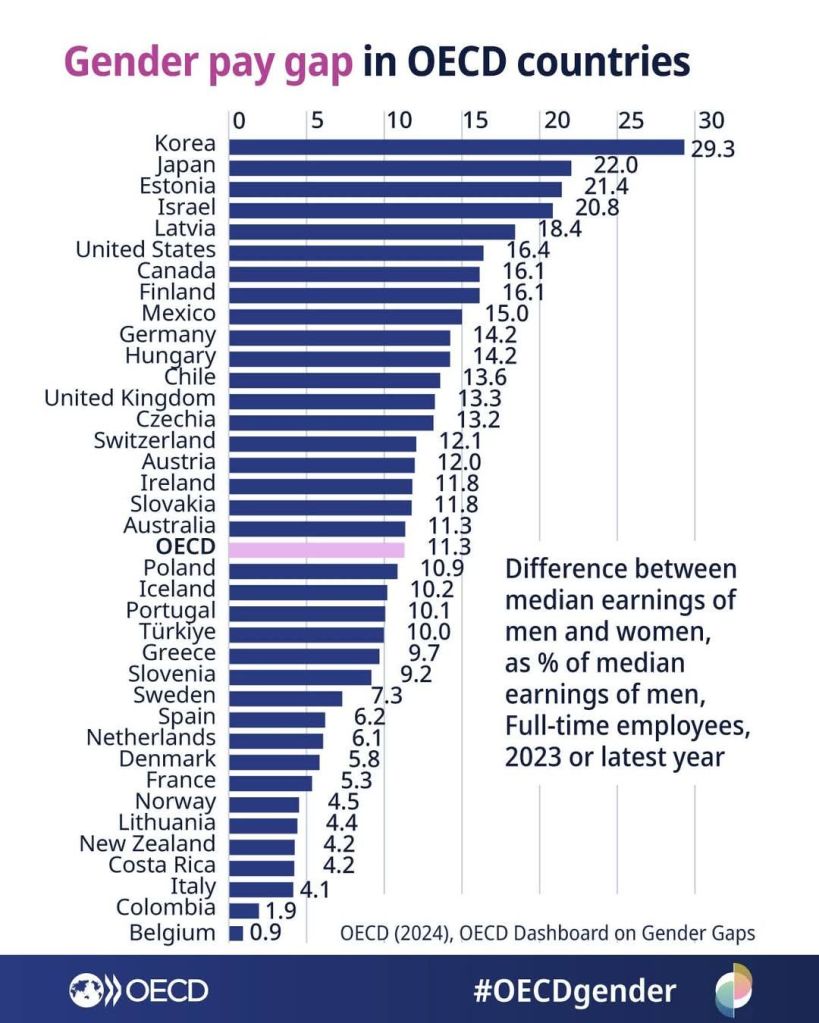
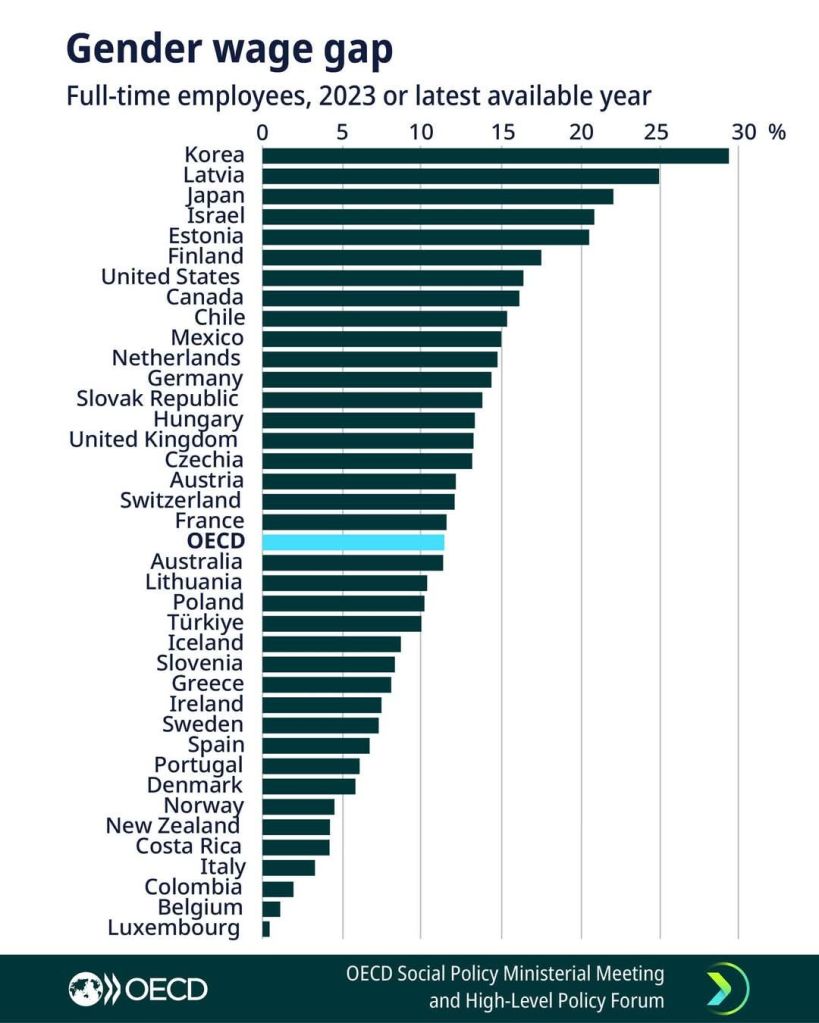
Minimal gender wage gap in NZ!
30 Mar 2025 Leave a comment
in discrimination, econometerics, economics of education, gender, human capital, labour economics, labour supply, occupational choice, politics - New Zealand, poverty and inequality Tags: gender wage gap, sex discrimination
People Barely Care About Equality
27 Mar 2025 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, economics of education, human capital, income redistribution, labour economics, labour supply, poverty and inequality, Public Choice, rentseeking, urban economics Tags: regressive left
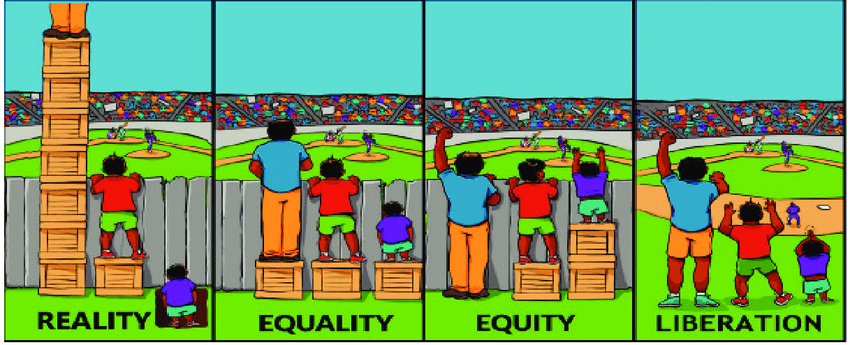
Another simple proof.
People Barely Care About Equality
What does India want – and what is New Zealand willing to give?
25 Mar 2025 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, comparative institutional analysis, development economics, economic history, economics of education, growth disasters, growth miracles, human capital, income redistribution, industrial organisation, international economic law, international economics, labour economics, labour supply, occupational choice, politics - New Zealand, poverty and inequality, Public Choice, rentseeking, survivor principle Tags: India, preferential trade agreements
Chris Trotter writes – What does India want from New Zealand? Not our dairy products, that’s for sure, it’s got plenty of those. Indeed 45 percent of the Indian population are small-scale farmers, most of them running a few head of cattle – not to eat, you understand – but to milk. If it once […]
What does India want – and what is New Zealand willing to give?
Book Nook Reading Notes on *Selfish Reasons to Have More Kids*
22 Mar 2025 Leave a comment
in economics of crime, economics of education, human capital, labour economics, labour supply, law and economics, occupational choice, poverty and inequality Tags: College premium, signaling

Bet On It reader Dan Barrett wrote these notes for his Book Nook book club on my Selfish Reasons to Have More Kids: Why Being a Great Parent Is Less Work and More Fun Than You Think. Dan’s idea:I’m organizing reading groups packaged as the Book Nook to help colleagues (1) guide their own learning…
Book Nook Reading Notes on *Selfish Reasons to Have More Kids*
Quotation of the Day…
19 Mar 2025 Leave a comment
in economic history, labour economics, poverty and inequality Tags: The Great Enrichment
Tweet… is from page 172 of the 2012 revised edition of Steven Landsburg’s great 1993 book, The Armchair Economist: [I]ncome statistics don’t account for everything we value. For one thing, we care about the quantity and quality of our leisure time. Here it’s by and large the poor who have made great strides, while the…
Quotation of the Day…
Jane Austen was wrong: women don’t marry up for money and status
10 Mar 2025 1 Comment
in economics of love and marriage, economics of marriage, human capital, labour economics, law and economics, poverty and inequality Tags: dating markets, gender wage gap, marriage and divorce, sex discrimination
A new study debunks the myth of the gold-digging wife, finding that women are no more likely to marry above their social class than menBy Ben Spencer, Science Editor of The Sunday Times. Excerpts:”The young pretty women who seek to “marry up” for money and status, from the Bennet sisters in Pride and Prejudice to…
Jane Austen was wrong: women don’t marry up for money and status
15 years of US research on the minimum wage elasticity of employment
04 Mar 2025 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, econometerics, economic history, economics of regulation, labour economics, labour supply, minimum wage, poverty and inequality
It’s time to pick up my recent thread of posts on the minimum wage (most recently in this post). I want to return for a moment to more conventional research on the minimum wage, specifically looking at the effects of higher minimum wages on employment. The majority of minimum wage research has focused on estimating…
15 years of US research on the minimum wage elasticity of employment
Gender gap
25 Feb 2025 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, discrimination, gender, health and safety, human capital, labour economics, labour supply, occupational choice, poverty and inequality Tags: gender wage gap
Gender gaps in education and declining marriage rates
06 Feb 2025 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, econometerics, economics of love and marriage, economics of marriage, human capital, labour economics, law and economics, poverty and inequality Tags: assortative mating, economics of fertility
Over the past half-century, the share of men enrolled in college has steadily declined relative to women. Today, 1.6 million more women than men attend four-year colleges in the U.S. This trend has not lowered marriage rates for college women, a substantial share of whom have historically married economically stable men without college degrees. Both […]
Gender gaps in education and declining marriage rates
By 2025 we were supposed to have closed the gap
05 Feb 2025 Leave a comment
in economic growth, economics of regulation, entrepreneurship, human capital, industrial organisation, labour economics, labour supply, macroeconomics, politics - New Zealand, poverty and inequality
Don Brash and Michael Reddell write – When Don was young and Michael’s parents were young, New Zealand had among the very highest material standards of living in the world. It really was, in the old line, one of the very best places to bring up children. But no longer. For 75 years now, with […]
By 2025 we were supposed to have closed the gap
Technological Disruption in the Labor Market
02 Feb 2025 Leave a comment
in econometerics, economic history, human capital, industrial organisation, labour economics, labour supply, occupational choice, poverty and inequality, unemployment Tags: creative destruction
By David J. Deming, Christopher Ong, and Lawrence H. Summers. From NPR’s Planet Money. Summers was Secretary of the Treasury from 1999 to 2001, director of the National Economic Council from 2009 to 2010 and president of Harvard University from 2001 to 2006.”Obviously, there is a big fear right now that artificial intelligence will kill…
Technological Disruption in the Labor Market
When did sustained economic growth begin?
31 Jan 2025 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, econometerics, economic growth, economic history, history of economic thought, labour economics, labour supply, macroeconomics, poverty and inequality Tags: The Great Enrichment
The subtitle is New Estimates of Productivity Growth in England from 1250 to 1870, and the authors are Paul Bouscasse, Emi Nakamura, and Jón Steinsson. Abstract: We estimate productivity growth in England from 1250 to 1870. Real wages over this period were heavily influenced by plague-induced swings in the population. Our estimates account for these […]
When did sustained economic growth begin?
My 92nd St. Y debate with Robert Kuttner on income inequality
29 Jan 2025 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, entrepreneurship, human capital, income redistribution, industrial organisation, labour economics, labour supply, liberalism, Marxist economics, politics - USA, poverty and inequality, Public Choice Tags: top 1%
Here goes: Ex po st, the Manhattan audience swung thirty (!) points in my favor, compared to the pre-debate poll. This was a fun event for me.
My 92nd St. Y debate with Robert Kuttner on income inequality
Recent Comments