Milton Friedman used to advise researchers to focus on large policy changes rather than attempting to separate a small change’s signal from the noise. In this sense, the “ambitious” policy agenda of the Biden-Harris administration was expected to be a gift to the research community. Accepting this gift, since 2020 I have been making forecasts…
Biden-Harris policies and their consequences were no surprise to those paying attention
Biden-Harris policies and their consequences were no surprise to those paying attention
30 Oct 2024 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, applied welfare economics, budget deficits, business cycles, econometerics, economic growth, economic history, economics of bureaucracy, economics of regulation, energy economics, entrepreneurship, environmental economics, financial economics, fiscal policy, global warming, health economics, income redistribution, industrial organisation, law and economics, macroeconomics, monetary economics, politics - USA, property rights, Public Choice, public economics, rentseeking Tags: 2024 presidential election, drug lags, taxation and entrepreneurship, taxation and investment
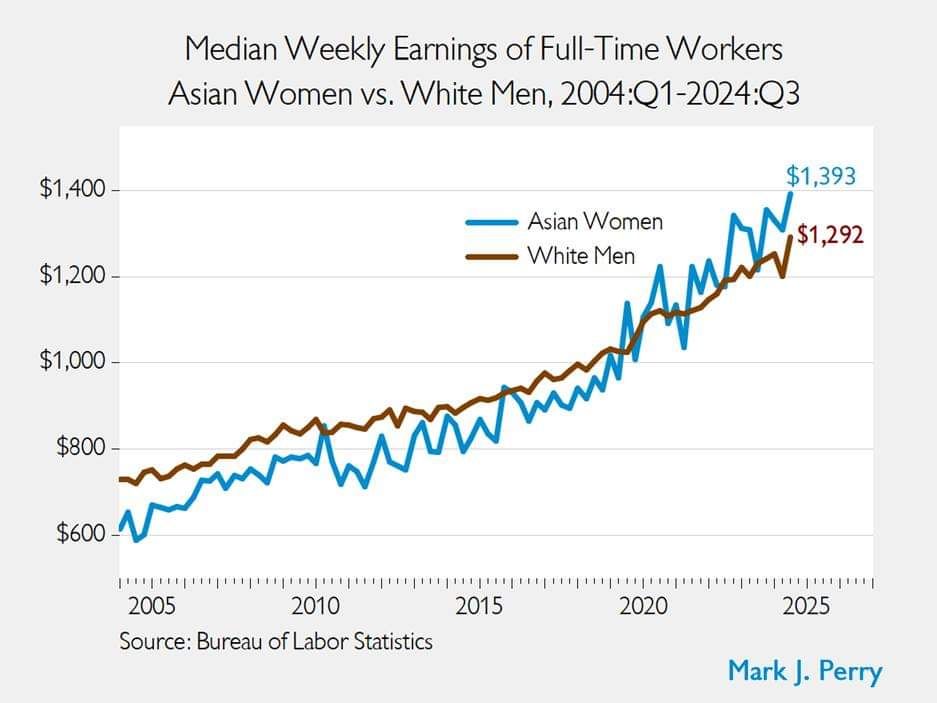
The gender gap that dare not speak its name
18 Oct 2024 Leave a comment
in discrimination, econometerics, economic history, economics of education, gender, human capital, labour economics, labour supply, occupational choice, poverty and inequality Tags: gender wage gap, racial discrimination
Fatal Flaw Discredits IPCC Science
08 Oct 2024 Leave a comment
in econometerics, energy economics, environmental economics, global warming

By way of John Ray comes this Spectator Australia article A basic flaw in IPCC science. Excerpts in italics with my bolds and added images. Detailed research is underway that threatens to undermine the foundations of the climate science promoted by the IPCC since its First Assessment Report in 1992. The research is re-examining the […]
Fatal Flaw Discredits IPCC Science
US Productivity Growth: Downside, Upside
08 Oct 2024 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, econometerics, economic growth, economic history, entrepreneurship, history of economic thought, industrial organisation, labour economics, labour supply, macroeconomics Tags: The Great Enrichment
Over time, a rising US standard of living is driven by productivity growth. Michael Peters succinctly describes the problem in “America Must Rediscover Its Dynamism” (Finance & Development, September 2024). He writes: The US economy has a multitrillion-dollar problem. It’s the dramatic slowdown in productivity growth over the past couple of decades. Between 1947 and…
US Productivity Growth: Downside, Upside
The Economic Consequences of the French Wealth Tax
17 Sep 2024 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, econometerics, economic history, entrepreneurship, fiscal policy, human capital, income redistribution, labour economics, labour supply, macroeconomics, occupational choice, poverty and inequality, Public Choice, public economics Tags: taxation and entrepreneurship, taxation and investment, taxation and labour supply
By Eric Pichet, here is the abstract: Despite attempts to ‘unwind’ the Impôt de Solidarité sur la Fortune (‘Solidarity Wealth Tax,’ the French wealth tax) during the last legislature (2002-2007), ISF yields had soared by 2006, jumping from €2.5 billion in 2002 to €3.6 billion. Analysis of the economic consequences of this ISF wealth tax […]
The Economic Consequences of the French Wealth Tax
Interview with Greg Mankiw: New Keynesian Macro, Growth, and Economic Policy
04 Sep 2024 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, budget deficits, business cycles, development economics, econometerics, economic growth, economic history, Edward Prescott, fiscal policy, great depression, history of economic thought, labour economics, law and economics, macroeconomics, Milton Friedman, monetarism, monetary economics, politics - USA, Public Choice, Robert E. Lucas, unemployment
Jon Hartley interviews Greg Mankiw on topics including New Keynesian macroeconomics, growth, and economic policy more broadly at his Capitalism and Freedom website (August 20, 2024, video and transcript available). Here are a few of the comments that caught my eye. On big models and small models in studying the macroeconomy: [O]n the issue of…
Interview with Greg Mankiw: New Keynesian Macro, Growth, and Economic Policy
It is wonderful to put inefficient firms out of business
31 Aug 2024 1 Comment
in applied price theory, econometerics, economic history, entrepreneurship, history of economic thought, industrial organisation, survivor principle Tags: creative destruction
The differences between the most and least productive companies can be startlingly high. By one estimate, in the US alone the most productive firms in a sector can be more than two to four times more cost-effective than the least productive ones. Given the size of those discrepancies, any expansion of trade or innovation that makes […]
It is wonderful to put inefficient firms out of business
Fiscal and monetary policy
27 Aug 2024 Leave a comment
in budget deficits, business cycles, econometerics, economic growth, economic history, financial economics, fiscal policy, history of economic thought, inflation targeting, macroeconomics, monetary economics, politics - New Zealand Tags: monetary policy

Over the last few years, The Treasury seems to have been toying with bidding for a more significant role for fiscal policy as a countercyclical stabilisation tool It seemed to start when Covid hubris still held sway – didn’t we do well? – and the first we saw of it in public was at a […]
Fiscal and monetary policy
Roger Pielke Jr. details ‘The Top Five Climate Science Scandals’: Study claiming no ‘climate crisis’ retracted ‘for not for being wrong…but instead for expressing views that are politically unhelpful’
18 Aug 2024 1 Comment
in econometerics, economics of education, energy economics, environmental economics, global warming Tags: climate activists, climate alarmism
What matters is what happens when mistakes are made.
Roger Pielke Jr. details ‘The Top Five Climate Science Scandals’: Study claiming no ‘climate crisis’ retracted ‘for not for being wrong…but instead for expressing views that are politically unhelpful’
Finally, exchange rate models seem to work pretty well
14 Aug 2024 Leave a comment
in budget deficits, business cycles, econometerics, economic history, financial economics, history of economic thought, inflation targeting, macroeconomics, monetary economics, politics - USA Tags: exchange rates, monetary policy
Exchange-rate models fit very well for the U.S. dollar in the 21st century. A “standard” model that includes real interest rates and a measure of expected inflation for the U.S. and the foreign country, the U.S. comprehensive trade balance, and measures of global risk and liquidity demand is well-supported in the data for the U.S. […]
Finally, exchange rate models seem to work pretty well
Basic income, again
09 Aug 2024 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, econometerics, labour economics, labour supply, poverty and inequality, unemployment, welfare reform Tags: universal basic income
This week’s column for the Stuff papers covered the excellent new US work testing the effects of a UBI. From November 2020, 3000 low-income people were randomly assigned into two groups for three years. One thousand people each received $1000 per month in unconditional funds for three years. Two thousand people each received $50 per month.Both…
Basic income, again
Frank DiTraglia on how to read econometrics papers
31 Jul 2024 Leave a comment
in econometerics, history of economic thought
Reading economics research papers is hard work when you are doing it for the first time as a graduate student. That’s why I try to get as many undergraduate students as possible engaged in some ‘inspectional reading’ (a term I learned from Marc Bellamare’s book Doing Economics, which I reviewed here), through the Waikato Economics Discussion…
Frank DiTraglia on how to read econometrics papers
The Minimum Wage, Rent Control, and Vacancies or Who Searches?
31 Jul 2024 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, comparative institutional analysis, econometerics, economic history, economics of regulation, income redistribution, labour economics, labour supply, law and economics, minimum wage, politics - USA, property rights, Public Choice, regulation, rentseeking, unemployment, urban economics Tags: housing affordability, regressive left, rent control

In an interesting new paper Federal Reserve economists Marianna Kudlyak, Murat Tasci and Didem Tüzemen look at what happens to job vacancy postings when the minimum wage increases. The vacancy data in our analysis come from the job openings data from the Conference Board as a part of its Help Wanted OnLine (HWOL) data series. […]
The Minimum Wage, Rent Control, and Vacancies or Who Searches?

Recent Comments