Piketty presents the changes in the top marginal income tax rate throughout the 20th century… #GCLIS http://t.co/sFpV0ypC5C—
LIS (@lisdata) April 16, 2014
Top marginal income tax rate throughout the 20th century
29 Jun 2015 Leave a comment
in economic history, entrepreneurship, income redistribution, politics - USA, Public Choice, public economics, rentseeking Tags: Eurosclerosis, taxation and entrepreneurship, taxation and investment, taxation and the labour supply, top 1%
Who taxes average workers most out of Australia, New Zealand, the USA and UK?
23 Jun 2015 Leave a comment
in fiscal policy, macroeconomics, politics - Australia, politics - New Zealand, politics - USA, population economics, public economics Tags: Australia, British economy, New Zealand, taxation and the labour supply
Figure 1: Direct taxes on the average worker in Australia, New Zealand, USA and UK, 2001 – 2012
Source: OECD Factbook 2014
Taxes on the average worker measure the ratio between the amount of taxes paid by the worker and the employer on the country average wage and the corresponding total labour cost for the employer. This tax wedge measures the extent to which the tax system on labour income discourages employment.
The taxes included in the measure are personal income taxes, employees’ social security contributions and employers’ social security contributions. For the few countries that have them, it also includes payroll taxes. The amount of these taxes paid in relation to the employment of one average worker is expressed as a percentage of their labour cost (gross wage plus employers’ social security contributions and payroll tax).
An average worker is defined as somebody who earns the average income of full-time workers of the country concerned in Sectors B-N of the International Standard Industrial Classification (ISIC Rev. 4). The average worker is considered single without children, meaning that he or she does not receive any tax relief in respect of a spouse, unmarried partner or child.
The impact of top tax rates on the migration of superstars
22 Jun 2015 Leave a comment
in human capital, labour economics, labour supply, occupational choice, politics - Australia, politics - New Zealand, politics - USA, public economics, sports economics Tags: British economy, CEO pay, Denmark, economics of migration, endogenous growth theory, Spain, superstar wages, taxation and entrepreneurship, taxation and superstars, taxation and the labour supply, Thomas Piketty, top 1%
Emmanuel Saez is leading a literature showing how sensitive migration decisions of superstars are to top marginal tax rates. Specifically, he and his co-authors studied Spain’s Beckham’s law.
Cristiano Ronaldo moved from Manchester United to Real Madrid in 2009 partly to avoid the announced 50% top marginal income tax in the UK to benefit from “Beckham Law” in Spain. Beckham’s Law was a preferential tax scheme of 24% on foreign residents in Spain. When David Beckham transferred to Real Madrid, the manager of Arsenal football club commented that the supremacy of British soccer was at risk unless the U.K.’s top marginal tax rate changed.
A number of EU member states offer substantially lower tax rates to immigrant football players, including Denmark (1991), Belgium (2002) and Spain (2004). Beckham’s law had a big impact in Spain:
…when Spain introduced the Beckham Law in 2004, the fraction of foreigners in the Spanish league immediately and sharply started to diverge from the fraction of foreigners in the comparable Italian league.
Moreover, exploiting the specific eligibility rules in the Beckham Law, we show that the extra influx of foreigners in Spain is driven entirely by players eligible for the scheme with no effect on ineligible players.

Suez also found evidence from tax reforms in all 14 countries that the location decisions of players are very responsive to tax rates. Suez in another paper with Thomas Piketty wants the top tax rate to be 80%. However, their work on taxation and the labour supply supports a much lower rate:
First, higher top tax rates may discourage work effort and business creation among the most talented – the so-called supply-side effect. In this scenario, lower top tax rates would lead to more economic activity by the rich and hence more economic growth. If all the correlation of top income shares and top tax rates documented on Figure 1 were due to such supply-side effects, the revenue-maximising top tax rate would be 57%.
Suez and Piketty then go on to argue that the pay of chief executives of public companies, a subset of the top 1% and top 0.1%, may not reflect their productivity but that is a much more complicated argument about agency costs and the separation of ownership and control which they make rather weakly.
Much of their other work on top incomes is about the emergence of a working rich whose top incomes are wages earned by holding superstar jobs in a global economy. It would be peculiar and perhaps overzealous to organise the entire taxation of high incomes around the correction of agency costs arising from the separation of ownership and control of some of the companies listed on the stock exchange.
Figure 1: Percentage of national income (including capital gains) received by top 1%, and each primary taxpayer occupation in top 1%, USA
Source: Jon Bakija, Adam Cole and Bradley T. Heim “Jobs and Income Growth of Top Earners and the Causes of Changing Income Inequality: Evidence from U.S. Tax Return Data”.
There is a long history showing how the labour supply of sports stars is highly sensitive to top marginal income tax rates. For a very long time, boxing was the only really big-money sport for athletes:
The 1950s was the era of the 90 percent top marginal tax rate, and by the end of that decade live gate receipts for top championship fights were supplemented by the proceeds from closed circuit telecasts to movie theatres.
A second fight in one tax year would yield very little additional income, hardly worth the risk of losing the title. And so, the three fights between Floyd Patterson and Ingemar Johansson stretched over three years (1959-1961); the two between Patterson and Sonny Liston over two years (1962-1963), as was also true for the two bouts between Liston and Cassius Clay (Muhammad Ali) (1964-1965).
Then, the Tax Reform Act of 1964 cut the top marginal tax rate to 70 percent effective in 1965. The result: two heavyweight title fights in 1965, and five in 1966. You can look it up.
Ufuk Akcigit, Salome Baslandze, and Stefanie Stantcheva found that the migration of superstar inventors is highly responsive to top marginal tax rates.
#Braindrain is real, even quantifiable — as per NBER paper 21024. Geniuses don't tolerate extra taxes easily. http://t.co/HVP8uEFAfz—
Amity Shlaes (@AmityShlaes) June 07, 2015
Ufuk Akcigit, Salome Baslandze, and Stefanie Stantcheva studied the international migration responses of superstar inventors to top income tax rates for the period 1977-2003 using data from the European and US Patent offices.
our results suggest that, given a ten percentage point decrease in top tax rates, the average country would be able to retain 1% more domestic superstar inventors and attract 38% more foreign superstar inventors.

Emmanuel Saez and co-authors also found that a preferential top tax scheme for high earning migrants in their first three years in Denmark was highly successful in attracting highly skilled labour to that country:
…the number of foreigners in Denmark paid above the eligibility threshold (that is the group affected by the tax scheme) doubles relative to the number of foreigners paid slightly below the threshold (those are comparison groups not affected by the tax scheme) after the scheme is introduced.
This effect builds up in the first five years of the scheme and remains stable afterwards. As a result, the fraction of foreigners in the top 0.5% of the earnings distribution is 7.5% in recent years compared to a 4% counterfactual absent the scheme.
This very large behavioural response implies that the resulting revenue-maximising tax rate for a scheme targeting highly paid foreigners is relatively small (about 35%). This corresponds roughly to the current tax rate on foreigners in Denmark under the scheme once we account for other relevant taxes (VAT and excises).

This blog post was motivated by a courageous tweet about Tony Atkinson saying that increases in the top tax rate have little effect on the supply of labour! Not so.
Who is where on the Laffer curve?
20 Jun 2015 Leave a comment
in economic growth, fiscal policy, human capital, labour economics, labour supply, macroeconomics, politics - USA, public economics Tags: endogenous growth theory, EU, Eurosclerosis, laffer curve, optimal tax theory, taxation and entrepreneurship, taxation and investment, taxation and the labour supply
@asymmetricinfo paper:"How Far Are We From The Slippery Slope? The Laffer Curve Revisited" bit.ly/1HMhmqu http://t.co/D9IffNhd92—
Old Whig (@aClassicLiberal) April 20, 2015
% of workers working more than 50 hours per week across OECD
18 Jun 2015 1 Comment
in labour economics, labour supply, occupational choice Tags: compensating differentials, taxation and the labour supply
Figure 1: % of workers working more than 50 hours per week, OECD, 2013
Source: OECD Better Life Index 2015.
In which Anglo-Saxon country is full-time work not enough to escape family poverty on the minimum wage?
07 Jun 2015 1 Comment
in labour economics, minimum wage, politics - Australia, politics - New Zealand, politics - USA, population economics, poverty and inequality, welfare reform Tags: earned income tax credit, poverty traps, single parents, taxation and the labour supply, welfare state
Figure 1: Weekly working hours needed at minimum-wage to move above a 50% relative poverty line after taxes, mandatory social or private contributions payable by workers, and family benefits for lone parent with two children, Anglo-Saxon countries, 2013
Supply-side economics and the migration of inventors
07 Jun 2015 Leave a comment
in applied price theory, entrepreneurship, fiscal policy, human capital, labour economics, labour supply, occupational choice, politics - Australia, politics - New Zealand, politics - USA Tags: economics of migration, taxation and the labour supply
#Braindrain is real, even quantifiable — as per NBER paper 21024. Geniuses don't tolerate extra taxes easily. http://t.co/HVP8uEFAfz—
Amity Shlaes (@AmityShlaes) June 07, 2015
Which Anglo-Saxon country has the largest after-tax pay increase after a minimum wage increase?
06 Jun 2015 Leave a comment
in labour economics, minimum wage, welfare reform Tags: poverty traps, single parents, taxation and the labour supply, welfare reform, welfare state
Figure 1: Net gain after income taxes, Social Security contributions and benefit reductions after a 5% minimum wage increase for a lone parent family
Which Anglo-Saxon country has the highest after-tax minimum wage?
05 Jun 2015 Leave a comment
in labour economics, minimum wage, public economics Tags: Australia, British economy, Canada, Ireland, progressive taxation, taxation and the labour supply, welfare state
Figure 1: Minimum wage after income tax and social security contributions, US$ PPP, Anglo-Saxon countries, 2013
Hours worked per worker varies greatly across industrialised countries
20 May 2015 Leave a comment
Monday morning blues? Compare the avg number of #working hours in yr country per year. More: bit.ly/1JPVYQu http://t.co/r5MsELJr1n—
(@OECD) April 19, 2015
Swedosclerosis and the British disease compared, 1950–2013
03 May 2015 2 Comments
in economic growth, economic history, entrepreneurship, macroeconomics, Public Choice, public economics Tags: British disease, British economy, Margaret Thatcher, poor man of Europe, Sweden, Swedosclerosis, taxation and the labour supply, welfare state
In 1970, Sweden was labelled as the closest thing we could get to Utopia. Both the welfare state and rapid economic growth – twice as fast as the USA for the previous 100 years.
Of course the welfare state was more of a recent invention. Assar Lindbeck has shown time and again in the Journal of Economic Literature and elsewhere that Sweden became a rich country before its highly generous welfare-state arrangements were created
Sweden moved toward a welfare state in the 1960s, when government spending was about equal to that in the United States – less that 30% of GDP.
Sweden could afford to expand its welfare state at the end of the era that Lindbeck labelled ‘the period of decentralization and small government’. Swedes in the 60s had the third-highest OECD per capita income, almost equal to the USA in the late 1960s, but higher levels of income inequality than the USA.
By the late 1980s, Swedish government spending had grown from 30% of gross domestic product to more than 60% of GDP. Swedish marginal income tax rates hit 65-75% for most full-time employees as compared to about 40% in 1960. What happened to the the Swedish economic miracle when the welfare state arrived?
In the 1950s, Britain was also growing quickly, so much so that the Prime Minister of the time campaigned on the slogan you never had it so good.

By the 1970s, and two spells of labour governments, Britain was the sick man of Europe culminating with the Winter of Discontent of 1978–1979. What happened?

Sweden and Britain in the mid-20th century are classic examples of Director’s Law of Public Expenditure. Once a country becomes rich because of capitalism, politicians look for ways to redistribute more of this new found wealth. What actually happened to the Swedish and British growth performance since 1950 relative to the USA as the welfare state grew?
Figure 1: Real GDP per Swede, British and American aged 15-64, converted to 2013 price level with updated 2005 EKS purchasing power parities, 1950-2013, $US
Source: Computed from OECD Stat Extract and The Conference Board, Total Database, January 2014, http://www.conference-board.org/economics
Figure 1 is not all that informative other than to show that there is a period of time in which Sweden was catching up with the USA quite rapidly in the 1960s. That then stopped in the 1970s to the late 1980s. The rise of the Swedish welfare state managed to turn Sweden into the country that was catching up to be as rich as the USA to a country that was becoming as poor as Britain.
Figure 2: Real GDP per Swede, British and American aged 15-64, converted to 2013 price level with updated 2005 EKS purchasing power parities, detrended, 1.9%, 1950-2013
Source: Computed from OECD Stat Extract and The Conference Board, Total Database, January 2014, http://www.conference-board.org/economics
Figure 2 which detrends British and Swedish growth since 1950 by 1.9% is much more informative. The US is included as the measure of the global technological frontier growing at trend rate of 1.9% in the 20th century. A flat line indicates growth at 1.9% for that year. A rising line in figure 2 means above-trend growth; a falling line means below trend growth for that year. Figure 2 shows the USA growing more or less steadily for the entire post-war period. There were occasional ups and downs with no enduring departures from trend growth 1.9% until the onset of Obamanomics.
Figure 2 illustrates the volatility of Swedish post-war growth. There was rapid growth up until 1970 as the Swedes converged on the living standards of Americans. This growth dividend was then completely dissipated.
Swedosclerosis set in with a cumulative 20% drop against trend growth. The Swedish economy was in something of a depression between 1970 and 1990. Swedish economists named the subsequent economic stagnation Swedosclerosis:
- Economic growth slowed to a crawl in the 1970s and 1980s.
- Sweden dropped from near the top spot in the OECD rankings to 18th by 1998 – a drop from 120% to 90% of the OECD average inside three decades.
- 65% of the electorate receive (nearly) all their income from the public sector—either as employees of government agencies (excluding government corporations and public utilities) or by living off transfer payments.
- No net private sector job creation since the 1950s, by some estimates!
Prescott’s definition of a depression is when the economy is significantly below trend, the economy is in a depression. A great depression is a depression that is deep, rapid and enduring:
- There is at least one year in which output per working age person is at least 20 percent below trend; and
- there is at least one year in the first decade of the great depression in which output per working age person is at least 15 percent below trend; and
-
There is no significant recovery during the period in the sense that there is no subperiod of a decade or longer in which the growth of output per working age person returns to rates of 2 percent or better.
The Swedish economy was not in a great depression between 1970 and 1990 but it meets some of the criteria for a depression but for the period of trend growth between1980 and 1986.
Between 1970 and 1980, output per working age Swede fell to 10% below trend. This happened again in the late 80s to the mid-90s to take Sweden 20% below trend over a period of 25 years.
Some of this lost ground was recovered after 1990 after tax and other reforms were implemented by a right-wing government. The Swedish economic reforms from after 1990 economic crisis and depression are an example of a political system converging onto more efficient modes of income redistribution as the deadweight losses of taxes on working and investing and subsidies for not working both grew.
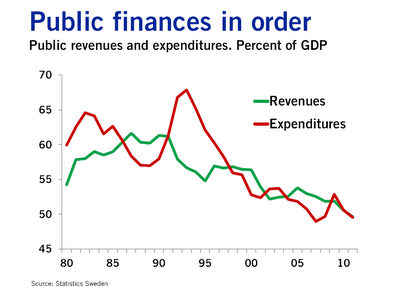
The Swedish economy since 1950 experienced three quite distinct phases with clear structural breaks because of productivity shocks. There was rapid growth up until 1970; 20 years of decline – Swedosclerosis; then a rebound again under more liberal economic policies.
The sick man of Europe actually did better than Sweden over the decades since 1970. The British disease resulted in a 10% drop in output relative to trend in the 1970s, which counts as a depression.

There was then a strong recovery through the early-1980s with above trend growth from the early 1980s until 2006 with one recession in between in 1990. So much for the curse of Thatchernomics?
After falling behind for most of the post-war period, the UK had a better performance compared with other leading countries after the 1970s.
This continues to be true even when we include the Great Recession years post-2008. Part of this improvement was in the jobs market (that is, more people in work as a proportion of the working-age population), but another important aspect was improvements in productivity…
Contrary to what many commentators have been writing, UK performance since 1979 is still impressive even taking the crisis into consideration. Indeed, the increase in unemployment has been far more modest than we would have expected. The supply-side reforms were not an illusion.
John van Reenen goes on to explain what these supply-side reforms were:
These include increases in product-market competition through the withdrawal of industrial subsidies, a movement to effective competition in many privatised sectors with independent regulators, a strengthening of competition policy and our membership of the EU’s internal market.
There were also increases in labour-market flexibility through improving job search for those on benefits, reducing replacement rates, increasing in-work benefits and restricting union power.
And there was a sustained expansion of the higher-education system: the share of working-age adults with a university degree rose from 5% in 1980 to 14% in 1996 and 31% in 2011, a faster increase than in France, Germany or the US. The combination of these policies helped the UK to bridge the GDP-per-capita gap with other leading nations.
The impact of the top tax rate in the depth and severity of the great depression
24 Apr 2015 Leave a comment
in business cycles, fiscal policy, great depression, macroeconomics, politics - New Zealand, politics - USA, public economics Tags: capital taxation, New Zealand, taxation and the labour supply, top tax rate
Source: Ellen McGrattan.
There were large differences in increases in the 1930s in the top marginal income tax rate between Sweden, the UK, France with Australia and New Zealand and between the USA and Canada and the rest as McGrattan explains:
These data show that there is a strong negative correlation, roughly −94%, between the change in the top income tax rates and the deviation in per capita real GDP relative to trend in 1933.
Average tax rates on consumption, investment, labour and capital in Australia and New Zealand, 1959-2011–updated
16 Apr 2015 1 Comment
in economic growth, fiscal policy, macroeconomics, politics - Australia, politics - New Zealand, public economics Tags: GST, lost decades, taxation and the labour supply, taxation of capital
Cara McDaniel went to the mammoth task of constructing average tax rates for 15 OECD countries over the period 1950-2003 for consumption, investment, labour and capital:
Total tax revenue is divided into revenue generated from four different sources: consumption expenditures, investment expenditures, labour income and capital income.
To find the average tax rate, tax revenue from each source is then divided by the appropriate income or expenditure base.
She used that data to examine the role of taxes and productivity growth as forces influencing market hours. She used a calibrated growth model extended to include home production and subsistence consumption, both of which were key features influencing market hours. Her model was simulated for 15 OECD countries. She found the primary force driving changes in market hours is found to be changing labour income tax rates and productivity catch-up relative to the United States is found to be an important secondary force.
I thought I would summarise the tax rate data computed by Cara McDaniel for Australia and New Zealand.
Source: Cara McDaniel.
McDaniel’s data on average tax rates on household incomes in Australia and New Zealand suggests that the average tax rate New Zealand household incomes fell by a third since 1986. No estimates were calculated for earlier years for New Zealand.
As for Australia, taxes steadily increased between 1959 and 1987 stabilised until 2005 and then fell a bit.
Source: Cara McDaniel.
There is a big spike in the average tax rate on consumption expenditure in New Zealand in 1986 when a GST replaced the pre-existing sales taxes. The average tax rate on New Zealand consumption expenditures and tapered away until the end of2009 and started to increase again.
Not much happened in Australia regarding the average tax rate in consumption expenditures since about 1983 despite the introduction of a GST in 1998.
Source: Cara McDaniel.
The average tax rate in capital income in Australia is much higher than in New Zealand. On the other hand, the average tax rate on investment expenditure is much higher New Zealand as compared to Australia.
Source : Cara McDaniel.
Taxes on investment expenditures increased quite significantly at the same time that a GST was introduced in New Zealand.
All in all, New Zealand cut taxes on personal income but that tax cut seemed to be pretty much offset by higher taxes on personal consumption through the introduction of a 10% and then 12.5% GST.
The most interesting finding in this database is the sharp increase in the average tax on investment expenditures in the mid-1980s. This prolonged New Zealand’s lost decades – the two decades of next to no GDP growth per working age New Zealander.
Real GDP per New Zealander and Australian aged 15-64, converted to 2013 price level with updated 2005 EKS purchasing power parities, 1956-2013
Source: Computed from OECD Stat Extract and The Conference Board, Total Database, January 2014.
New Zealand’s lost decades ended when the average tax rate on investment expenditures started to fall.
















Recent Comments